The so-called EMC is: the ability of a device or system to work properly in its electromagnetic environment without posing an unacceptable electromagnetic disturbance to anything in the environment. EMC testing includes two aspects: testing the intensity of electromagnetic disturbance sent to the outside world to confirm compliance with the limits specified in the relevant standards; and testing the sensitivity under electromagnetic environment conditions that specify the intensity of electromagnetic disturbance, so that Confirm compliance with the immunity requirements specified in the relevant standards. For engineers and technicians who are engaged in the design of single-chip application systems, it is necessary to master certain EMC testing techniques. 1 single chip system EMC test (1) Test environment In order to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the test results, the electromagnetic compatibility measurement has high requirements for the test environment, and the measurement site has an outdoor open space, a shielded room or an anechoic chamber. (2) Test equipment Electromagnetic compatibility measuring equipment is divided into two categories: one is electromagnetic interference measuring equipment, the equipment can be connected to the appropriate sensor to measure electromagnetic interference; the other is in electromagnetic sensitivity measurement, the equipment simulates different interference sources, through appropriate The coupling/decoupling network, sensor or antenna is applied to various types of devices under test for sensitivity or interference measurement. (3) Measurement method Electromagnetic compatibility testing is based on different standards, there are many kinds of measurement methods, but can be divided into four categories; conducted emission test, radiation emission test, conduction sensitivity (immunity) test and radiation sensitivity (immunity) test. (4) Test diagnostic steps (5) Test preparation 1 Test site conditions: EMC test laboratory is a radio wave semi-dark room and a shielded room. The former is used for radiation emission and radiation sensitivity tests, and the latter is used for conducted emission and conduction sensitivity tests. 2 Environmental level requirements: The level of the electromagnetic environment for conduction and radiation is preferably well below the limits specified by the standard, and the ambient level is generally at least 6 dB below the limit. 3 test tables. 4 Isolation of the measuring device from the device under test. 5 Sensitivity Criteria: Generally provided by the testee, and monitored and discriminated in real time, the degree of performance degradation is determined by means of measurement and observation. 6 Placement of the device under test: In order to ensure the repeatability of the experiment, the placement of the device under test is usually specified. (6) Test types Conducted emission test, radiation transmission test, conducted immunity test, radiation immunity test. (7) Common measuring instrument Electromagnetic interference (EMI) and electromagnetic sensitivity (EMS) tests require the use of many electronic instruments such as spectrum analyzers, electromagnetic field disturbance meters, signal sources, function amplifiers, and oscilloscopes. Due to the wide EMC test frequency (20Hz ~ 40GHz), large amplitude (μV level to kW level), many modes (FM, AM, etc.), many postures (flat, oblique, etc.), the correct use of electronic instruments is very important. A suitable instrument for measuring electromagnetic interference is a spectrum analyzer. A spectrum analyzer is an instrument that displays the law of voltage amplitude as a function of frequency. The waveform displayed is called the spectrum. The spectrum analyzer overcomes the shortcomings of the oscilloscope in measuring electromagnetic interference, and can accurately measure the interference intensity at each frequency. The spectrum analyzer can directly display the various spectral components of the signal. The most important issue in solving electromagnetic interference problems is to determine the source of the interference. Only when the interference source is accurately located can the measures to resolve the interference be proposed. Determining the source of interference based on the frequency of the signal is the easiest method because the frequency characteristics are most stable among all the characteristics of the signal, and the circuit designer tends to be very clear about the signal frequencies at various parts of the circuit. Therefore, as long as the frequency of the interference signal is known, it can be estimated which part of the interference is generated. For electromagnetic interference signals, because the amplitude is often much smaller than the normal working signal, it is very simple to do this measurement with a spectrum analyzer. Since the spectrum analyzer has a narrow intermediate frequency bandwidth, it is possible to filter out signals different from the interference signal frequency and accurately measure the interference signal frequency to determine the circuit that generates the interference signal. FUME EXTRA 1500PUFFS Shenzhen Xcool Vapor Technology Co.,Ltd , http://www.xcoolvapor.com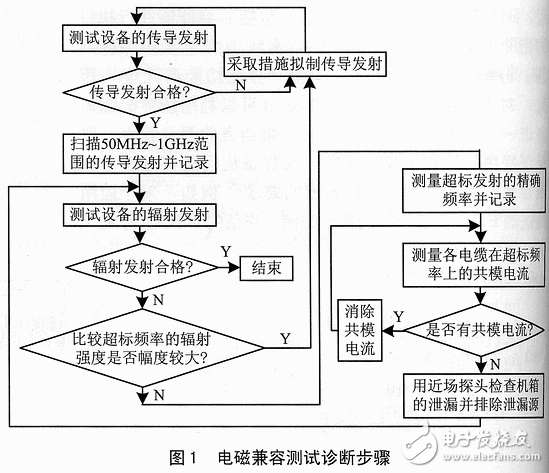
May 08, 2024