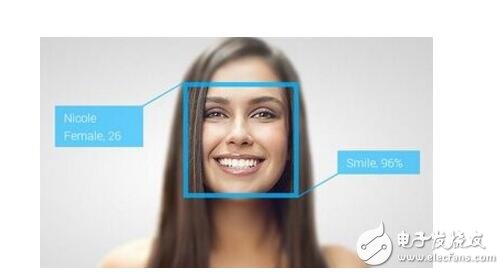
Face recognition is a biometric recognition technology based on human facial feature information for identification. A series of related techniques for capturing a face or a video stream with a camera or a camera, and automatically detecting and tracking the face in the image, and then performing face detection on the detected face, which is also commonly called portrait recognition and face recognition. Non-mandatory: the user does not need to cooperate with the face collection device, and the face image can be obtained almost in an unconscious state. Such sampling method is not “mandatoryâ€; Non-contact: Users can obtain facial images without direct contact with the device; Concurrency: In the actual application scenario, multiple face sorting, judgment and recognition can be performed; In addition, it also meets the visual characteristics: the characteristics of “seeing peopleâ€, as well as the features of simple operation, intuitive results and good concealment. Face recognition is mainly divided into three processes: face detecTIon, feature extracTIon and face recogniTIon. Face detection: Face detection refers to detecting and extracting a face image from an input image. Usually, the haar feature and the Adaboost algorithm are used to train the cascade classifier to classify each block in the image. If a rectangular area passes through the cascade classifier, it is discriminated as a face image. Feature extraction: Feature extraction refers to the representation of face information by some numbers, which are the features we want to extract. Common facial features are divided into two categories, one is geometric features and the other is characterized. Geometric features are geometric relationships between facial features such as the eyes, nose, and mouth, such as distance, area, and angle. Since the algorithm utilizes some intuitive features, the amount of computation is small. However, because its required feature points cannot be precisely selected, its application range is limited. In addition, when the illumination changes, the face has foreign objects obscured, and the facial expression changes, the feature changes greatly. Therefore, this type of algorithm is only suitable for rough recognition of face images and cannot be applied in practice. The characterization feature utilizes the gradation information of the face image to extract global or local features through some algorithms. One of the more commonly used feature extraction algorithms is the LBP algorithm. The LBP method first divides the image into several regions, and thresholds the center value in the pixel 640x960 neighborhood of each region, and regards the result as a binary number. Figure 3 shows an LBP operator. The LBP operator is characterized by a constant monotonic grayscale change. Each region obtains a set of histograms by such operations, and then joins all the histograms to form a large histogram and performs histogram matching calculation for classification. Face recognition: The face recognition mentioned here is a narrow face recognition, which compares the features extracted by the face to be recognized with the features of the face in the database, and discriminates the classification according to the similarity. Face recognition can be divided into two broad categories: one is confirmation, which is the process of comparing the face image with the existing image of the person in the database, answering whether you are your problem; The other type is recognition, which is the process of matching the face image with all the images already stored in the database, and answering who you are. Obviously, face recognition is more difficult than face recognition because identification requires a large amount of data matching. Commonly used classifiers include nearest neighbor classifiers, support vector machines, and the like. Face recognition is mainly used for identification. Since video surveillance is rapidly spreading, many video surveillance applications urgently need a fast identification technology in a long-distance, user-incompatible state, in order to quickly confirm the identity of a person at a long distance and realize intelligent early warning. Face recognition technology is undoubtedly the best choice. Fast face detection technology can be used to find faces in real time from surveillance video images and compare them with face database in real time to achieve fast identification.
DIP Sockets & Adapters
Precision machined Dual In-line Package (DIP) Sockets and Adapters accommodate applications from surface mount to thru-hole. Screw-machined terminals offer superior quality for long-term durability. DIP Sockets Adapters,DIP Integrated circuit Sockets,Dual In-line Package Sockets,Dual In-line Package Adapters,IC Socket, IC Sockets Adapters ShenZhen Antenk Electronics Co,Ltd , https://www.antenksocket.com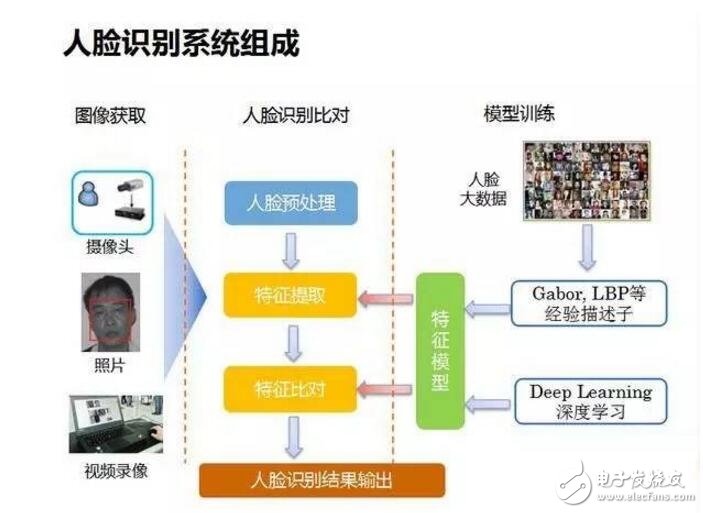
Overview of DIP Sockets & Adapters
DIP Sockets and Adapters allow for quick and easy device replacement, upgrade, or repair in test and production applications, while protecting DIP devices from exposure to heat during board processing. Screw-machined terminals with redundant, multi-finger contacts ensure reliable performance even in harsh environments.
Automated assembly compliant.
Wide range of patterns and terminal styles, from 8 to 64 pins.
Optional Tape Seal on terminals protects contacts from contaminants during board processing.
Solder Preform terminals available for mixed SMT and thru-hole process applications.
RoHS Compliant insulators and terminals are compatible with lead-free processing - select either Matte Tin/Gold (MG) or Gold/Gold (GG) plating.
Our large selection of DIP sockets ranging from 1 to 48 contacts can provide a highly reliable connection between your integrated circuit (IC) devices and PCBs. Antenk offers DIP sockets in a wide variety for high reliability. Positions range from 1 to 48, and termination options include through hole and surface mounting, solderless zero profile, four-finger inner contact and dual leaf contacts, as well as a variety of plating options.

Antenk DIP Sockets Product Features
1 to 48 positions
Precision four-finger inner contacts or dual leaf contacts are optional
Open frame and closed frame housings
Available with a variety of plating options
Four-Fingered Contacts
Precision machined or stamped four-finger inner contacts with open or closed frame housings facilitate highly reliable DIP sockets.
Dual Leaf Contacts
Dual leaf contacts provide a cost effective solution to the DIP socket design with superior handling characteristics.
Face recognition summary
Antenk DIP (Dual Inline Package) Sockets-Classic DIP Sockets
May 07, 2023