EMC test requirements are divided into three categories according to product use: military, industrial and commercial use, and residential and residential use. The latter two test items, requirements, methods, etc. are more consistent, the difference lies in the requirements of the indicators. The military category is quite different from the latter two because of its special use. In addition, due to the special use of aviation and marine equipment, in addition to the higher requirements of military equipment, there are international standard specifications. Based on the conditions of use of AC regulated power supplies sold in the market, this article focuses on the latter two categories. In view of the increasing concern about EMC issues in the society and the many professions and products involved, IEC has treated EMC requirements as the basic standard of IEC. This is the famous IEC61000 series of standards. This standard has been regarded internationally as a common standard as important as safety standards. One of the IEC61000-4 "Testing Techniques" is the basic standard for guiding EMC testing. Since EMC technology is a complex and constantly evolving new technology involving multiple disciplines, EMC test projects, requirements, and methods are constantly being revised and improved. Therefore, many of the projects in IEC61000-4 have not yet been officially released and are still in the draft. In order to facilitate the reader to understand this knowledge, we will introduce the project involving AC regulated power supply, and focus on the IEC project adopted by relevant national standards. IEC61000-4, full name "Electro magneTIc CompaTIbility for Electrical and Electronic Equipment, Part 4: TesTIng and Measurement Techniques", "Electromagnetic compatibility of electrical and electronic equipment - Part 4: Test techniques". Among them are 11 test items. The items and requirements related to the AC regulated power supply standard SJ/T10541-94 are as follows: IEC61000-4-4: Electrical Fast Transients (Burst) Immunity Test, SJ/T10541-94 and SJ/T10542-94 use this standard. The purpose of this project is to verify the immunity of the device to various transient disturbances caused by switching transients (inductive load interruptions, relay contact trips, etc.). The test severity level (interference generator (50Ω internal resistance) open circuit output test voltage at the power input end) is 1 level, 0.5kV; 2 levels, 1kV; 3 levels, 2kV; 4 levels 4kV. IEC61000-4-5Surge Transients Immunity Test (surge or surge). The content is temporarily in the draft. Related to this can be referred to the well-known IEC801-5 and the US standard IEEEstd 587-1980 "IEEE Guide for Surge Voltages in Low-Voltage AC Power ircuits" (IEEE Guide: Surge in a low-voltage AC power circuit). The electronic industry standards SJ/T10541-94 and SJ/T10542-94 cite some of this aspect. The purpose of the project is to verify the immunity of the equipment to high-energy surges caused by power switching and lightning. The severity level is divided as above, but the output impedance of the interference generator is 2Ω, while the former is 50Ω. The interference generator output separates the voltage voltage of 1.2 & TImes; 50μs (for high-resistance load) and short-circuit (discharge) current wave for 8 × 20μs (for low-resistance load). Similar test requirements are listed in many electrical and electronic product standards. In addition, high-frequency spike noise sensitivity tests are used internationally. Especially in Japan, this test is very common. The US military standard MILSTD461, 462 uses similar projects, but the noise simulation generator required to use much more power than the former. There are similar standards in China, such as the 50 kHz to 100 MHz power line conduction sensitivity test in GB4859-84; the CS06 item in GJB151-86 and GJB152-86, the noise is rectangular pulse wave. In addition, GB6162-85 (refer to IEC255-4) uses attenuated oscillating waves. SJ/T10541-94 and SJ/T10542-94 suggest that one of these two methods can be arbitrarily selected. The purpose of the project is the same as IEC61000-4-4. The rectangular pulse wave is characterized by fast rise and low repetition rate, and the characteristic of the damped oscillation wave is high amplitude and low energy. For products containing digital circuits, rectangular pulse waves are more sensitive to interference. Projects related to electromagnetic interference include power frequency harmonic limit requirements, conducted interference and radiation interference limit requirements. SJ/Z9029.2-87 (equivalent to IEC555-2-1982) specifies the harmonic current limit values ​​required for equipment in low-voltage power supply systems. For high-power semiconductor converters, GB/T3859.2-93 limits the maximum power capacity (the ratio of the short-circuit capacity of the power system to the apparent power of the converter's fundamental wave) for different converters (by pulse number). Current harmonics. It must be pointed out that electricians and electronic products have been identified as power pollution through the power line to the mains, and the requirements for this are to be strengthened as the "environmental protection" of the mains system. The judgment of the EMC test results, the anti-interference test and the electromagnetic interference test are respectively used in completely different ways. The latter uses the quantitative limit value as the qualified threshold decision point; the former is generally determined by qualitative methods, that is, according to the performance classification of the product in the test (take GB/T13926-92 as an example): Class a: In the product performance index specification (within tolerance), the performance is normal; Class b: Temporary reduction or loss of function or performance, but self-recovery; Class c: Temporary reduction or loss of function or performance, but requiring operator intervention or system reset; Class d: Reduced or lost functionality that is unrecoverable due to damage. Among the four categories, class a is qualified, and class d is unqualified. For class b and class c, the qualification is determined by the manufacturer and the user according to the specific circumstances. Naturally, the technical measures taken for these two types are different. It seems that the judgment of the immunity test is too loose, which is actually the principle of the maximum degree of freedom of the standard. Because of the wide variety of devices under test and the large differences, it is difficult to make universal quantitative regulations for the qualification. Of course, a certain evaluation standard should be given for a specific type of product. SJ/T10541-94 embodies this requirement. The converter type of converter is similarly specified in GB/T3859.1-93, as the basis for the qualification judgment. The standard defines level 3, namely: Class F: Performance level, which refers to a combination of all kinds of electrical disturbance limits that the converter can withstand without degrading performance; Class T: Trip level refers to the combination of all kinds of electrical disturbance limit values ​​that the converter can withstand without interrupting the operation due to the protection device action; it can be further divided into two cases: the automatic reclosing after interference in the past and the inability to Automatic reclosing (to be manually used, etc.); Class D: Damage level is a combination of all electrical disturbance limits that the converter can withstand without causing permanent damage. Obviously, the F level here is equivalent to the class A, the class D is equivalent to the class d, and the class T is the class b and class c. For the AC regulated power supply with anti-interference function requirements specified in SJ/T10541, in addition to ensuring normal operation, the load should be given a suitable sensitivity threshold at the output; the interference residual voltage superimposed on the output voltage is specified. The peak value should not be greater than 20% of the nominal value of the output voltage. This is the purpose principle of the standard compliance standard, fully considering the essential difference between the AC stabilized power supply and other electrical and electronic products in terms of functional requirements. That is, the former should serve the latter, and the former also serves as the power filter for the latter power EMI. The purpose is to provide sufficient EMI safety margin for EMI-sensitive equipment and improve the immunity level of the equipment. According to the provisions of GB6833.4, the requirements of the electronic instrument for the transient sensitivity of the power supply are: it should be able to withstand 20% of the transient voltage shock of the nominal source voltage change without causing malfunction. For this reason, the maximum allowable transient voltage value (sensitivity threshold) is specified in SJ/T10541 as the output of the AC regulated power supply when receiving the immunity test. In addition, considering that the AC regulated power supply is to provide suitable AC voltage conditions for electronic equipment, SJ/T10541 also stipulates that the relative deviation (ie, output effect) of the output voltage of the AC regulated power supply should be in its reference during the immunity test. Within the condition (tolerance G), this is used as a basis for determining whether or not performance is degraded. The combination of the two, in a scientific, reasonable, practical, easy-to-operate way, solves the problem of no quantitative indicators based on the specific assessment and conformity assessment of the anti-interference performance of the AC stabilized power supply. However, the general standard only uses the general error, performance degradation or degradation as the basis for assessment and conformity assessment. Obviously, this qualitative method is not easy to operate. The items measured by EMI are measured by power conduction below 30 MHz and radiated by 30-1 GHz. The following objectives must be achieved in the measurement instrument settings at RBW = 9K (for conduction) & 120 kHz (for Radiation). This environment must be measured in a condition where the background noise is extremely low or the environment where the external interference source is isolated. (Example) CISPR 11/CISPR22 Message Level B Test Standard 5.08MM Wire To Board Connectors
5.08MM Wire To Board Connectors
5.08 mm Wire to Board connectors are avialable in different terminations and sizes intended for use on a variety of applications. These connectors provide power and signal with different body styles, termination options, and centerlines. To find the wire to board set required, click on the appropriate sub section below.
5.08mm Wire To Board Connectors Type
5.08mm Terminal
5.08mm Wire To Board Connectors Advantages
5.08 mm Wire To Board Connectors Application
5.08MM Wire To Board Connectors ShenZhen Antenk Electronics Co,Ltd , https://www.antenkconn.com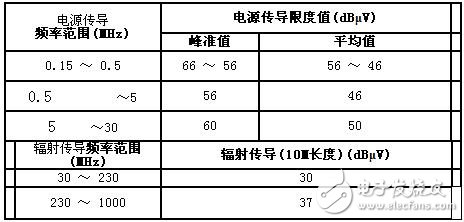
5.08mm Housing
Pitch 5.08mm Wafer Right Angle&SMT Type
5.08mm Wafer Straight Type
5.08mm Wafer SMT Type
5.08mm Wafer Right Angle Type
5.08mm Wafer Single Row Straight Type
5.08mm Wafer Single Row SMT Type
5.08mm Wafer Double Row Straight Type
5.08mm Wafer Double Row SMT Type
5.08mm Wafer Double Right Angle Type
5.08mm Wafer Double Right Angle&SMT Type
Small electronics with high current requirements
One of the strongest advantage of the Micro Fit series is its applicability in delivering the high current requirement in electronics with supplying high power.
Safe and Reliable
ensure safety, system protection and performance with its bonded metallic conduits and multiple grounding points preventing fire hazards, component damage, overheating and possible electrocution.
ROHS Compliant
The product does not contain restricted chemicals in concentrations not complying with ROHS standards. Thus, for its components, the products can be worked upon at high temperatures required by lead-free soldering.
Motherboard Connectors
The Motherboard of a computer holds together many of the crucial components such as the central processing unit (CPU), memory and connectors for input and output devices. Microfit connectors ensure high performance electronic system in quality motherboards.
You can easily find Scondar`s Microfit in most ITX Motherboards, in which its functionality is best described for solid performance in a small footprint, and low power consumption (less than 100 Watts).
Printer Connectors
The 5.08mm Microfit can also be seen in most printers
Automotive PC Connectors
Smart, high power automotive PC power supply garners its capabilities from quality Microfit connectors, designed for general purpose battery powered applications. These are manufactured to provide power and to control the motherboards' switch based on ignition status.
Solar Panels
Microfit can also be commonly found in a solar array. A solar array is connected to each other, and to inverters through connectors to produce a successful flow of electricity.
June 15, 2023