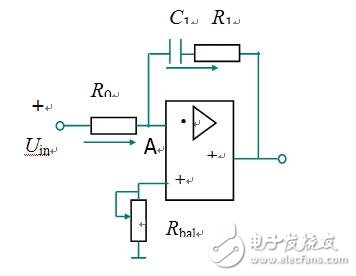
The PI regulator is a linear controller that forms a control deviation according to a given value and an actual output value. The proportional and integral of the deviation are linearly combined to form a control quantity, and the controlled object is controlled. Learn the basics of PI regulators, circuits and other pi regulators. The PI regulator is a linear controller that forms a control deviation according to a given value and an actual output value, and linearly combines the proportional (P) and integral (I) deviations to form a control amount to control the controlled object. Proportional adjustment: proportional to the deviation of the reaction system, once the system has a deviation, the proportional adjustment immediately produces a regulation to reduce the deviation. The proportional effect is large, which can speed up the adjustment and reduce the error, but the excessive proportion makes the stability of the system drop, and even causes the instability of the system. Integral adjustment: The system eliminates the steady-state error and improves the no-difference. Because there is an error, the integral adjustment is performed until there is no difference, the integral adjustment stops, and the integral adjustment outputs a constant value. The strength of the integral action depends on the integral time constant TI. The smaller the TI, the stronger the integral action. On the other hand, when TI is large, the integral action is weak, and adding integral adjustment can reduce the stability of the system and slow the dynamic response. The integral action is often combined with the other two adjustment rules to form a PI regulator or a PID regulator. P is the ratio, I is the integral, and the effect of the integral is based on the amount of deviation. The role of the ratio is to speed up the convergence. From the principle of automatic control, PI adjustment does not bring the characteristic value of the right half plane, so it will not cause system oscillation, but the PI adjustment is based on the proportional amplification of the deviation, so after the deviation disappears, the PI adjustment loses its effect, resulting in PI adjustment is not No difference adjustment system with limited accuracy. (1) Proportional adjustment function: According to the deviation of the proportional reaction system, once the deviation occurs in the system, the proportional adjustment immediately produces a regulation to reduce the deviation. The proportional effect is large, which can speed up the adjustment and reduce the error, but the excessive proportion makes the stability of the system drop, and even causes the instability of the system. (2) Integral adjustment function: The system eliminates the steady-state error and improves the no-difference. Because there is an error, the integral adjustment is performed until there is no difference, the integral adjustment stops, and the integral adjustment outputs a constant value. The strength of the integral action depends on the integral time constant TI, and the smaller the Ti, the stronger the integral action. On the other hand, when Ti is large, the integral action is weak, and the integration adjustment can reduce the stability of the system and slow the dynamic response. The integral action is often combined with the other two adjustment rules to form a PI regulator or a PID regulator. Question: What if you want high steady-state accuracy and fast dynamic response? As long as the combination of proportional and integral control is combined, this is the proportional integral control. PI regulator In analog electronic control technology, an operational amplifier can be used to implement the PI regulator, the circuit of which is shown below. Proportional integral (PI) regulator 2. PI regulator transfer function When the initial condition is zero, the Laplace transform on both sides of the above formula is taken, and after the shift term, the transfer function of the PI regulator is obtained. 3. PI regulator output time characteristics Time characteristics of the output voltage of the PI regulator Analysis result It can be seen that the proportional integral regulator combines the advantages of both the proportional control and the integral control, and overcomes their respective shortcomings, and fosters strengths and weaknesses and complements each other. The proportional part responds quickly to the control and the integral part eventually eliminates the steady-state deviation. Therefore, the PI regulator has been widely used.
Navigator speaker:
Navigator speaker is a kind of micro speaker unit which uses a diaphragm made of Mylar material. Mylar speakers are of ultrathin design and lightweight and clear voice. It is widely used in car electronics (GPS navigator, digital video recorder, radar detector-).
There are two types of Mylar speakers from the shapes:
1) Round shapes, we have products from 10mm to 57mm in diameter.
2) Oblong shape, we have products in sizes of 1510/1712/1813-..
FAQ
Q1. What is the MOQ? Navigator Speaker,Gps Speaker,Radar Speaker,Vehicle Navigation Speakers Shenzhen Xuanda Electronics Co., Ltd. , https://www.xdecspeaker.com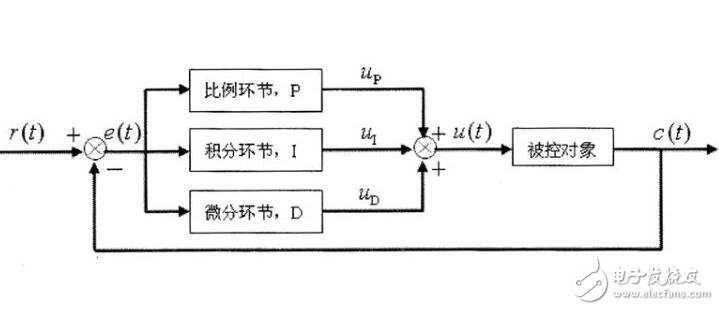
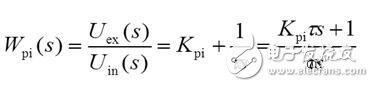
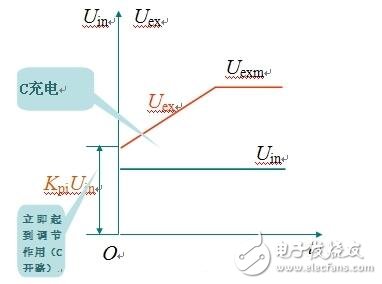
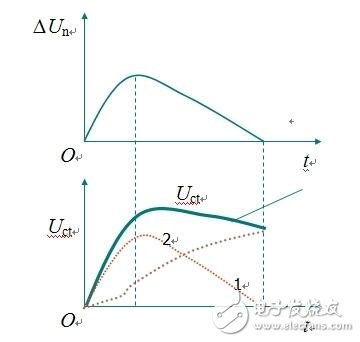
Input and output dynamic process of PI regulator



XDEC: 2000pcs for one model.
Q2. What is the delivery lead time?
XDEC: 15 days for normal orders, 10 days for urgent orders.
Q3. What are the payment methods?
XDEC: T/T, PayPal, Western Union, Money Gram.
Q4. Can you offer samples for testing?
XDEC: Yes, we offer free samples.
Q5. How soon can you send samples?
XDEC: We can send samples in 3-5 days.
October 27, 2022