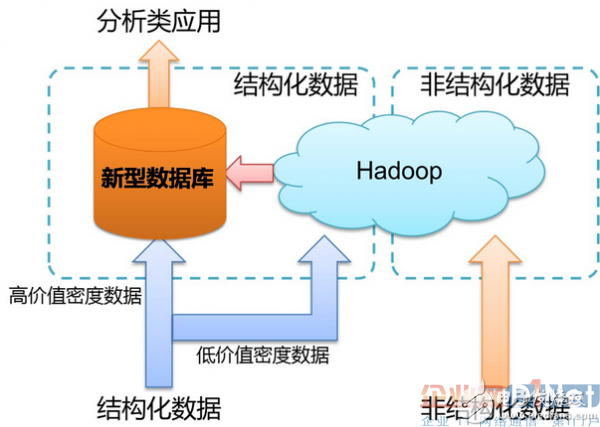
The field of big data has developed rapidly and is very hot in the past five years, but in general it is still in its infancy. In this seminar, I will talk about data and the pressure of big data on data processing technology, and then share with you why there are many innovations in data processing technology in recent years. 1. Discovery and use of data values Among the four Vs of big data, the most significant feature should be Value. Regardless of the size of the data, what structure, source, and data that can bring value to the user is the most important data. I have been dealing with data for more than 20 years, and I have never felt that the status of data is so high today. The whole society's perception of data has changed. The biggest contribution of big data is at least to make all levels of society begin to realize the importance of data, including the top leaders and the bottom people. At present, everyone basically agrees that data is a valuable asset like oil and coal, and its intrinsic value is very huge. Another significant contribution is undoubtedly the ingenious use and value of data by Internet companies. 2. Review of data processing technology The "big" data on the Internet is an indisputable fact. Now analyze the challenges faced by data processing technology. In addition to Internet companies, the field of data processing is still the world of traditional relational databases (RDBMS). The core design philosophy of traditional RDBMS was basically formed 30 years ago. What has stood out in the past 30 years is undoubtedly Oracle. The database market in the world is basically monopolized by Oracle, IBM/DB2, and Microsoft/SQL Server, and other market shares are relatively small. SAP acquired Sybase last year and wants to be a database vendor. A small number of independent database vendors now have Oracle and Teradata. The open source database is mainly MySQL, PostgreSQL, and other industries except the Internet field. These databases were mainly designed and developed for OLTP transactional requirements, and were used to develop human-machine session applications. The physical storage format of these traditional databases is row storage, which is more suitable for frequent additions, deletions and changes of data. However, for statistical analysis queries, row storage is actually inefficient. Among these mature database products, there are two typical exceptions: one is Teradata and the other is Sybase IQ. Teradata used the MPP (Massive Parallel Processing) architecture from the beginning to provide customers with software and hardware products. Its positioning is high-end customer data warehouse and decision analysis system. Teradata has only a few thousand customers worldwide. In this high-end market for data analysis, Teradata has always been the boss. In data analysis technology, Oracle and IBM can't beat Teradata. Sybase IQ is the first relational database product based on column storage. Its location is similar to Teradata, but it is sold in software. Teradata and Sybase IQ are generally better than Oracle, DB2, etc. in performance analysis. 3. Data growth accelerates, data diversification, the era of big data is coming If it is now the era of big data, it is actually a qualitative change in the source of data. Before the advent of the Internet, data was mainly generated by human-computer conversations, with structured data as the mainstay. So everyone needs a traditional RDBMS to manage these data and applications. At that time, the data growth was slow, the system was relatively isolated, and the traditional database could basically satisfy various application development. The emergence and rapid development of the Internet, especially the development of the mobile Internet, coupled with the large-scale use of digital devices, the main source of data today is not a human-machine session, but is automatically generated by devices, servers, and applications. The data of the traditional industry has also increased. The data is mainly unstructured and semi-structured, and the actual transaction data volume is not large, and the growth is not fast. Machine-generated data is growing at a geometric level, such as genetic data, various user behavior data, positioning data, images, video, weather, earthquakes, medical, and more. The so-called "big data application" is mainly to sort, cross-analyze and compare various types of data, and deeply mine the data to provide self-service impromptu and iterative analysis capabilities for users. Another type is the feature extraction of unstructured data, as well as the content retrieval and understanding of semi-structured data. Traditional databases have little to no problem with such requirements and applications, both technically and functionally. This in fact provides a good development opportunity and space for Hadoop-like technologies and platforms. Internet companies naturally choose open source technologies that support their business, which in turn drives the rapid development of open source technologies. 4. New data processing technologies, products and innovations In response to the pressure of data processing, there has been a lot of innovation and development in the field of data processing technology in the past decade. In addition to the high-concurrency, short-transaction OLTP memory database (Altibase, Timesten), other technological innovations and products are oriented to data analysis, and large-scale data analysis, can also be said to be big data analysis. In these innovations and products for data analysis, in addition to various NoSQL based on Hadoop environment, there is a new type of database product (called NewSQL) based on Shared Nothing architecture for structured data analysis, such as: Greenplum ( EMC acquisition), Vertica (HP acquisition), Asterdata (TD acquisition), and GBase 8a MPP Cluster developed by Nanda GM in China. There are dozens of similar open source and commercial products that can be seen at present, and new products are constantly emerging. An interesting phenomenon is that most of these new database vendors have not been 10 years old, and the basic development has been acquired. Companies that acquire these new database vendors, such as EMC and HP, are hoping to enter the big data processing market by acquiring new technologies and products, and are new players. In addition to acquiring Sybase, SAP has developed a new product called HANA, which is an in-memory, data-oriented, in-memory database product. The commonalities of these new analytical database products are: The architecture is based on large-scale distributed computing (MPP); the hardware is based on X86 PC servers; the storage is based on the local hard disk that comes with the server; the operating system is mainly Linux; it has extremely high scale out and inherent fault tolerance and Data high availability guarantee mechanism; can greatly reduce the processing cost per TB of data, providing technical and cost-effective support for "big data" processing. In general, data processing technology has entered a new wave of innovation and development, with many opportunities. The main reason here is that traditional database technology, which has been in use for 30 years, has encountered technical bottlenecks, and the needs of the market and users are driving technological innovation and creating many opportunities for this. In the face of big data, more and more users are willing to try new technologies and new products, which is not so conservative, because everyone begins to clearly see the bottleneck of traditional technology, and it is possible to solve new problems that they face by choosing new technologies. The overall trend now is that under the pressure of rapid growth in data volume and the coexistence of multiple types of data analysis, data processing technology is moving in the direction of subdivision. The era of one platform meeting all application requirements has passed in the past 30 years. We must start to choose the most suitable products and technologies to support the application based on application needs and data volume. The world data processing market is undergoing revolutionary changes. The traditional database (OldSQL) has become a situation in which OldSQL+NewSQL+NoSQL+ other new technologies (streaming, real-time, memory, etc.) support multiple applications. In the era of big data, what is needed is the choice of data-driven optimal platforms and products. 5. MPP relational database and Hadoop non-relational database There are three types of big data storage technology routes: The first is a new type of database cluster using MPP architecture, focusing on industry big data, using Shared Nothing architecture, through column storage, coarse-grained index and other big data processing technologies, combined with efficient distributed computing mode of MPP architecture. Support for analysis applications, the operating environment is mostly low-cost PC Server, with high performance and high scalability, and has been widely used in enterprise analysis applications. This type of MPP product can effectively support structured data analysis at the PB level, which is not possible with traditional database technology. For the enterprise's new generation of data warehouse and structured data analysis, the best choice at present is the MPP database. Figure 1 MPP architecture diagram The second is based on Hadoop's technology extension and encapsulation. Derived related big data technology around Hadoop, dealing with data and scenarios that are difficult to handle in traditional relational databases, such as storage and calculation of unstructured data, making full use of Hadoop. The advantages of open source, along with the continuous advancement of related technologies, will gradually expand its application scenarios. At present, the most typical application scenario is to support and support the big data storage and analysis of the Internet by extending and encapsulating Hadoop. There are dozens of NoSQL technologies in it, which are further subdivided. The Hadoop platform is better at unstructured, semi-structured data processing, complex ETL processes, complex data mining and computational models. The third is the Big Data All-in-One, a combination of software and hardware designed for the analysis and processing of big data. It consists of a set of integrated servers, storage devices, operating systems, database management systems, and data queries. High-performance big data all-in-one machine with good stability and vertical scalability. 6. The importance of data warehousing Before the rapid development of the Internet, both telecom operators, big banks, and insurance companies spent huge sums of money to establish their own enterprise-level data warehouses. These warehouses are mainly used to generate some key indicators (KPIs) for enterprises, and some enterprises have thousands or even tens of thousands of KPI reports, such as daily, weekly, and monthly. These systems have several main features: The technical architecture is mainly based on the traditional RDBMS + minicomputer + high-end array (that is, IOE), of course, the database has some DB2, Teradata and so on. Reports are basically fixed static reports, generated in the form of T+1 (can not be generated immediately). The amount of data growth is relatively slow, and the environmental changes of DW are few. End users can only view aggregated reports, and rarely do dynamic drilldown based on aggregated data. Most leaders basically think that they have spent a lot of money, but they don't see whether it is worth doing or not. Finally, everyone turned a blind eye to a large number of reports. This type of system belongs to “Gao Fu Shuai†and is used by wealthy enterprises for leadership. Finally, most companies and departments currently do not have a data warehouse at all. In fact, the analysis of traditional data has not been done very well, has not been popularized, and now it has encountered big data. Data warehousing is really useful for businesses, and the key is how to use the data well. 7. What is the core issue of data processing technology? In fact, we have been facing the most core and biggest problem in data processing, that is, performance issues. Technologies and products with poor performance are not viable. The problem of data processing performance is not due to the emergence of big data, nor the disappearance of big data technology. The improvement of processing performance will promote the mining and use of data value, and the more and deeper the data value mining, the higher the processing technology requirements. The current data warehouse can only meet some static statistical requirements, and it is the T+1 mode. It is also because of performance problems that operators cannot effectively construct big data warehouses beyond the PB level, and cannot provide ad hoc queries, self-service analysis, and complex model iterative analysis. The ability to make a large number of front-line personnel use data analysis. Today, if you do a "big data" data warehouse, the challenges faced by operators are much larger than in the last 10 years. There is currently no single technology and platform that can meet the data analysis needs of similar operators. The alternative solution can only be a mashup architecture that uses a different distributed technology to support a data warehouse system that goes beyond the PB level. The main core of this mashup architecture is a new generation of MPP parallel database clusters + Hadoop clusters, plus some memory computing, and even stream computing technology. Big data needs a multitude of technologies to support it. The current data processing challenges for enterprises are growing, mainly for the following reasons: The first reason is that the amount of data is already an order of magnitude higher than the previous generation, and a provincial-level operator can surpass 1PB structured data in one year. The second reason is that "big data" is more concerned with user behavior, group trends, correlations between events, etc., not just past KPIs. This puts new requirements and challenges on the data analysis platform's ability to analyze data and performance. Figure 2 The core technology of future big data processing 8. Summary - the value of the new MPP database Technology: The new database based on column storage + MPP architecture has a huge difference in core technology from traditional databases. It is designed for structured data analysis and can effectively handle PB level data. Technically solved data processing performance problems for many industry users. User value: The new database runs on x-86 PC servers and can significantly reduce the cost of data processing (one order of magnitude). Future trends: The new database will gradually be used in conjunction with the Hadoop ecosystem to process PB-level, high-quality structured data with MPP, while providing rich SQL and transaction support for applications; semi-structured, unstructured with Hadoop Data processing. This meets the processing needs of both structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. Mv Power Cable,Armor Mv Cable,Steel Tape Armor Cable,Sta Medium Voltage Cable Baosheng Science&Technology Innovation Co.,Ltd , https://www.bscables.com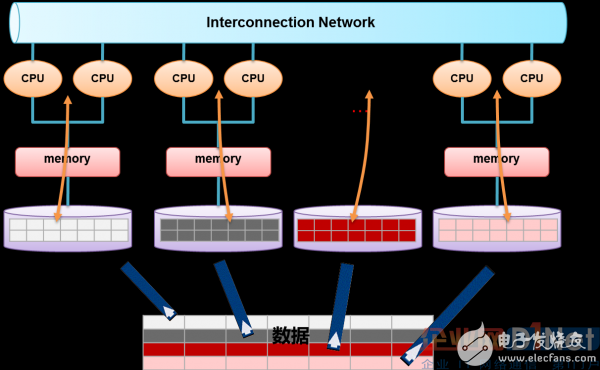
January 19, 2023