1. Direction: Selecting different light sources, controlling and adjusting the direction of incident light on the object is the most basic parameter of the machine vision system design. It depends on the type of light source and the position placed relative to the object. 2. Spectral: Light is composed of a single or multiple component spectrum. For example, the spectrum of sunlight is composed of all spectra from infrared to ultraviolet. The spectrum that the human eye can sense is between 380 nm and 780 nm. Red 780nm to purple 380nm. The color of the light depends on the type of light produced by the light source and the optical filter that covers the light source or camera lens. 3. Polarization: (PolarizaTIon), also known as polarized light, is a characteristic of light waves. When light propagates, it is oscillated like electromagnetic waves. The direction of oscillation of ordinary light waves is uncertain, and the direction of oscillation of polarized light is uncertain. On a defined plane, for example, the axis of oscillation of the linearly polarized light is perpendicular to the direction of propagation. This directionality of the light wave retains this polarization in the specularly reflected light, while the diffuse reflected light is lost. This allows the use of the polarization of the light to cause specular glare across the camera lens to eliminate the effects of specular light. Intensity: The intensity of the light will affect the exposure of the camera. If the light is insufficient, it means low contrast. If you increase the magnification, you may enlarge the noise at the same time, or increase the aperture of the lens, but the depth of field is reduced. Is it possible to dissipate heat? In turn, the intensity is too much to waste energy and bring heat to the problem. Uniformity: Uniform illumination is required in all machine vision applications, as all sources vary in distance as the distance increases and the illumination angle deviates, so when illuminated for large areas, Larger problems sometimes only keep the center of the field of view uniform. 1. Reflection characteristics: The performance of reflecting incident light from an object has two very different reflection characteristics. 1) Mirror reflection: The angle of reflection of light is equal to the angle of incidence. Mirror reflections are sometimes very versatile and can sometimes produce extreme glare. Specular reflection should be avoided in most cases. 2), diffuse: the light shining on the object diffuses out from all directions. In most practical cases, diffuse light is formed over a range of angles and depends on the angle of the incident light. 2. Color: The color observed by the human eye or camera may be formed in three different ways: 1) Adding color: The effect of combining light of two or three wavelengths into light of a certain wavelength, for example, a mixture of yellow light (wavelength of 620 nm) and blue light (wavelength of 480 nm), the effect of green light appears, but actually The green portion of the spectrum does not have the energy of this spectral segment. Using this characteristic of light, a color television was invented, and the three primary colors of red, green and blue in the television monitor can basically synthesize various colors of nature. 2), subtractive color: When reflecting, remove some wavelengths of light from the spectrum. White light containing all visible spectra, after illuminating a red object, the red spectrum is reflected and other components are absorbed by the object. For example, white metals such as steel and yellow metals such as gold. The difference in color between them is because the steel reflects the light of all the spectra more uniformly, while the gold reflects the white light, but the blue light is subtracted from it, and the yellow color appears. 3. Optical Density: Objects of different materials, different thicknesses or different chemical properties have different transmittances when light passes through them. This difference may exist throughout the spectral range or it may only exist at certain points in the spectrum. In general, backlighting is the best way to detect differences in optical density. 4. Refraction: Different transparent substances have different folding rates. They transmit incident light in different directions. For example, the refractive indices of air and glass are different. When the directional light is irradiated in a certain direction, the bubbles in the glass bend the light so that a black or bright bubble profile is produced. 5. Texture: The texture of the surface of the object may be useful in image processing; it may also be too thin to be resolved, but it will affect the reflection of light. Sometimes textures are important and should be enhanced with light, and sometimes textures are not needed. It can cause noise and should be dimmed to reduce the effects of texture. 6. Height: Features of different heights in the object can be enhanced with directional light or with diffused light to attenuate the effects of height. 7. Surface orientation: The difference in the relative direction of different parts of the surface of the object can be enhanced by directional light or by diffuse light. Our Fiber Optic Tools including Fiber Optic Tool Kits, Fiber Termination Tools: Fiber Splicing Tools, Fiber Network Tools, Crimp Tools, Fiber Connector Tool, Corning Fiber Tools, Fiber Stripping Tools, Cleaving Tools, Fiber Scribe Tools, Fiber Optic Mid-Access Tools, cable slitter, cable cutters, Kevlar cutters, optical connector removal tools, cable pulling tools, fiber optic work table, distance measuring wheels, heat gun and Fiber Optic Cable dispenser. Fiber Optic Tools, Fiber Cutter And Stripper, Fiber Cleaner, Fiber Susion Splicer, Fiber Optic Stripper, Fiber Splice Closure, Fiber optic Splice Boxes NINGBO YULIANG TELECOM MUNICATIONS EQUIPMENT CO.,LTD. , https://www.yltelecom.com
1) direct light: the incident light is basically from one direction, the angle of incidence is small, it can project the shadow of the object;
2) Scattered light: The incident light comes from multiple directions, even in all directions, it does not project a distinct shadow. 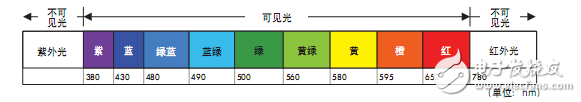
The color is distinguished directly from the wavelength of the illumination light. For example, the light at a wavelength of around 580 nm is green, and the light is used to illuminate the green object, thereby distinguishing between the object and the background; 
First, several elements of machine vision light source lighting technology
January 01, 2023