In order to synchronize the scan signal with the measured signal, the oscilloscope can set some conditions to continuously compare the measured signal with these conditions. Only when the measured signal meets these conditions, the scan is started, so that the frequency of the scan is The measured signals are the same or have an integer multiple of the relationship, that is, synchronization. This technique is called "triggering" and these conditions are called "trigger conditions".
1. Trigger releaseThe oscilloscope's trigger holdoff Hold Off is very important for stable display of Burst type waveforms. As shown in the figure below, if there is no Hold Off, the oscilloscope triggers the first pulse of the Burst waveform for the first time, and the third pulse of the Burst waveform is triggered for the second time, so that the screen does not see a stable Burst waveform. String, while shaking the waveform left and right. The oscilloscope uses Hold Off to solve this problem. When the oscilloscope is triggered for the first time, it must pass the Hold Off time before it can perform the second trigger. Thus, if the Hold Off time is set to be longer than the Burst waveform string, then the second time. The first pulse to the second Burst waveform is also triggered, so that the entire Burst waveform string can be stably displayed on the oscilloscope's screen.

Edge triggering is the most common and simplest and most effective triggering method. Most applications use edge triggering to trigger waveforms. The edge trigger is only the edge, polarity, and level of the signal. When the measured signal changes direction with the same level (rising edge or falling edge) and its value changes to the same level as the trigger level, the oscilloscope is triggered and captures the waveform. As shown in Figure 3, the always rising edge at the trigger point. The rising edge is triggered if the height of the trigger level is reached during the rising process. Otherwise, the waveform on the oscilloscope is still in the Normal mode, and the waiTIng for triggering is indicated in the lower right corner of the oscillating device.
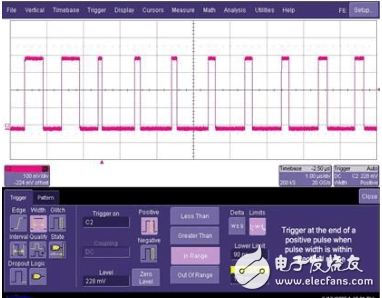
Trigger based on signal width value / glitch value, optional forward or negative width / glitch, can be used to capture rare width / glitch signals in the signal. The trigger setting of Figure 5 means that when the pulse width of C2 is between 90 ns and 120 ns at the trigger level, the position at which the trigger point stays is the falling edge of the pulse. If a negative pulse width is triggered, the position at which the trigger point stays is the rising edge of the pulse. The range of pulse widths can be defined as less than, greater than, within or outside the range. The glitch trigger is similar to the width trigger.
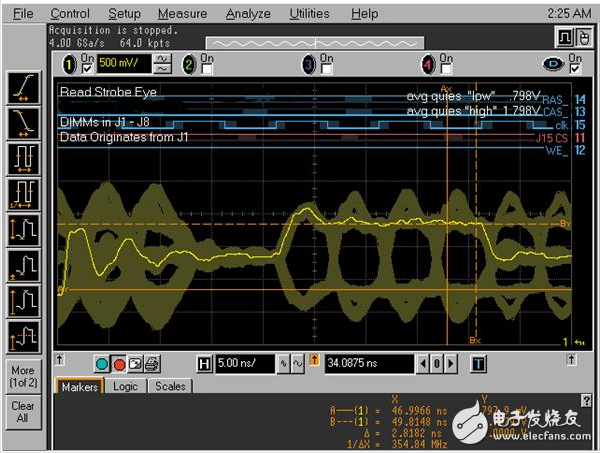
State triggering refers to adding a clock channel to determine the pattern on the basis of the pattern. The pattern can be judged by the rising edge of the clock, or the pattern can be judged by the falling edge of the clock, or both rising and falling can be judged. Pattern. State triggering is a very useful triggering feature, especially on hybrid oscilloscopes (mixed oscilloscopes typically have 16 logical channels and 4 analog channels). For example: trigger the read or write status of DDR, one channel is connected to the clock (the pattern is judged by the rising edge of the clock), other channels are connected to the command signal (such as: CS, WE, CAS, etc.), and the table is known to read and write the corresponding code. Type, you can stably trigger the read or write waveform. The following figure shows an example of capturing a “read†signal eye diagram using a mixed-signal oscilloscope. The logic channel forms a state trigger and the analog channel captures a “read†eye diagram.
The low level trigger is as shown in the figure below, which is well understood to trigger a short pulse or a runt pulse in a normal burst. You need to set the high and low thresholds to determine what is a short pulse (a pulse between the two thresholds is a short pulse). There are two types of options: positive short pulses and negative short pulses.

With the advancement of technology, LED technology has been applied to projectors. There are many good domestic LED projector manufacturers in the market. For example, Shenzhen Resources has perfectly combined this technology with DLP technology to make it portable and compact. Because of its low power consumption and heat generation, it is more widely used in life and in personal business. The same goes for LED hotel projectors.
portable led projector,led home theater projector,led holiday projector,led room light projector,led 4k projectors
Shenzhen Happybate Trading Co.,LTD , https://www.szhappybateprojectors.com