Things around us are becoming smarter. From cars to smartphones, to digital assistants, and even robots. We are not just talking about new and breakthrough new features every day. More importantly, devices, computers, and machines are all smartly performing tasks. How are they done? Through artificial intelligence, which is AI. The term "artificial intelligence" was first proposed by cognitive scientist John McCarthy in his research, he wrote, "This study is based on the assumption that any learning behavior or other intellectual characteristics can be accurately described in principle. So that a machine can be built to simulate it." This description still applies today, but the complexity has increased. You may have recently heard "artificial intelligence" and several other words appear at the same time, especially "machine learning" and "deep learning." They are often used interchangeably, and although they are related, they are not the same thing. This can be confusing. We explain the difference between artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning through a classic example: comparing apples and oranges. In a broad sense, artificial intelligence describes the various ways in which a machine interacts with the world around it. Through advanced, human-like intelligence—the result of a combination of software and hardware—an artificial intelligence machine or device can mimic human behavior or perform tasks like a human. We read a lot of things about artificial intelligence today, such as speech recognition (for smart personal assistant devices), facial recognition (used in filters that are popular on current social media), or object recognition (such as searching for apples and oranges). picture of). But how are these functions implemented? From a root point of view, machines equipped with artificial intelligence mimic human thinking processes, such as the ability to distinguish between apples and oranges. Machine learning is a way or subset of artificial intelligence that emphasizes "learning" rather than computer programs. A machine uses sophisticated algorithms to analyze large amounts of data, identify patterns in the data, and make a prediction—no one needs to write specific instructions in the machine's software. After mistakenly treating a cream puff as an orange, the pattern recognition of the system will improve over time as it will learn from mistakes and correct itself like a human being. Through machine learning, a system can learn from its own mistakes to improve its pattern recognition capabilities. Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that drives computer intelligence to make great strides. It uses a lot of data and computing power to simulate deep neural networks. Essentially, these networks mimic the connectivity of the human brain, classify data sets, and discover the correlation between them. If you have new learning knowledge (without manual intervention), the machine can apply its insights to other data sets. The more data the machine processes, the more accurate its predictions will be. For example, a deep learning device can check big data—such as the color, shape, size, maturity, and origin of the fruit—to accurately determine whether an apple is a green apple, and whether an orange is a blood orange. Through deep learning, machines can process large amounts of data, identify complex patterns, and provide insights. The difference between artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning is not as obvious as apples and oranges, they are more subtle. Qualcomm has integrated artificial intelligence technology into the Opteron mobile platform to create a compelling and intuitive experience that allows devices to learn more about you. LIFEPO4 Battery For Home Energy Storage Jiangsu Zhitai New Energy Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.zt-tek.com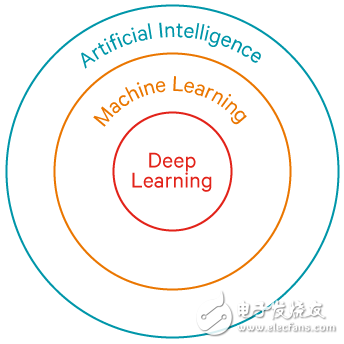

Recommend 54V (53.5V – 54.5V) for equation charge
(≤95%R.H.)
-20~65℃ discharge
S/N
Project
General Parameter
1
Number of series
15S
2
Rated voltage
48V
3
End of discharge voltage
40V
4
Charging voltage
Recommend 51V (50.5V – 51.5V) for floating charge
5
Continuous charge and discharge curren
≤100A
6
Internal resistance (battery pack)
≤100mΩ
7
Self-discharge rate
≤2%/month
8
range of working temperature
0~65℃ charge
9
Storage temperature range(≤95%R.H.)
-40~70℃
10
Positive and negative lead way
Fence Terminal 2P*2
11
Display screen
LED display, four physical buttons
12
Protective function
Overcharge, over discharge, short circuit, overload, over temperature, etc.
13
certificate
MSDS,ISO9001,CE,UN38.3,ROSH
March 15, 2023