If the current Internet of Things and applications are fragmented and local, then the future of the Internet of Things based on 5G technology is to bring together a large amount of data, massive devices, and Internet of Things with terminal intelligence. It can be said that it is based on 5G. The Internet of Things is a truly scalable and more economically valuable Internet of Things. And the 5G IoT trip did not start at the commercial origin in 2020, but now. Compared with the traditional communication industry development model, the development model of the Internet of Things is rich in change, and the vertical industry application and cross-domain integration are equally prosperous, so that China Telecom no longer uses the "ecological chain" to describe it, but replaces it with the "ecological cube." How to find the law of "Magic Cube", how to cut into the future of the Internet of Things, how to extend the advantage from the communication field to the Internet of Things field, this is the telecom operators, equipment, software service providers, until the terminal and chip companies are currently common Thinking about the problem. A few days ago, Qualcomm gave a preliminary answer - to promote the trend of non-mobile smart terminal marginalization, and to establish a platform to provide long-term communication connection services for these smart terminal devices. At present, the cost of intelligent technology is getting lower and lower, and its capabilities are getting stronger. It can be extended to the edge of the network, and even sensors can be intelligent. This trend has brought the originally centralized network center nodes closer to the edge of the network and closer to the physical world. Sensor devices at the edge of the network, at the edge of the cloud, and in contact with the physical world constitute intelligent marginalization. Shen Lei, senior director of Qualcomm product market, said in an interview with China Electronics News that 5G's vision is to provide services for all smart devices except mobile phones, covering various fields and vertical industries. According to Qualcomm, by 2020 The serviceable market outside the mobile phone reached 66 billion US dollars. A typical example of edge intelligence in the IoT market is the car. Shen Lei said that in the automotive field, Qualcomm has now signed more than $3 billion in orders, and this is only the beginning. Lu Yi, Managing Director of Cisco IoT China and Asia Pacific, told China Electronics News that more than 50% of the smart terminals connected to the Cisco IoT connection platform are cars, becoming the most active application area of ​​the Internet of Things. This development trend, Qualcomm is happy, and is helping to promote development. “So far, there are hundreds of brands and more than 1.5 billion smart devices equipped with IoT terminals for Qualcomm products.†Shen Lei said, “In the field of Internet of Things, our main partners include operators and Internet of Things providers. And some module level equipment vendors." Shen Lei believes that with the advancement of intelligence to the edge, and the arrival of a fully connected, all-intelligent world, Qualcomm can greatly benefit from its technical reserves in the mobile phone industry in the field of Internet of Things and other non-mobile phones, and through Mobile technology is recombined, re-integrated and re-launched and adapted for non-mobile handsets. These technologies include a variety of processing and computing power, such as CPU, GPU, DSP, and also include a variety of connectivity capabilities, such as Gigabit LTE, future 5G, low-power Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, etc., and perceptual capabilities. For example, the perception technology and ability of vision, hearing, location, etc., in addition, there are security capabilities. There are some essential differences between the Internet of Things field and the mobile phone field. Shen Lei summarized this difference into three aspects. One is that the equipment and application scenarios are different, the other is that the network deployment mode is different from the business model, and the third is that the ecosystem is different. After years of development, the mobile phone field has formed a clear ecosystem. From chip makers to mobile phone OEMs and ODMs, to operators or public channels, there are only two or three levels, and the mobile phone exchange rate is very high. However, the Internet of Things is completely different. It penetrates vertical industries, including industrial manufacturing, smart cities, and industrial applications. There are many forms of equipment and a long industrial chain. From chip vendors to module vendors, industry terminal integrators, and users in various fields. It also includes IoT service providers, and the Internet of Things is in the early stages of development, and the entire ecological and business operation model is in the process of exploration. Zhang Ying, chief engineer of the Shanghai Industrial and Information Committee, said in an interview with the China Electronics News during the "two sessions" this year that Shanghai has formed a three-year implementation opinion on the Internet of Things planning, and combined with Shanghai's overhead lines to work. Plan a package to make a new round of planning for the entire information infrastructure. In the pilot town of Shanghai, tens of thousands of sensors were installed at one time, but whoever manages, how to manage, how to protect funds, how to ensure safety, and how to ensure the safety certification of equipment are new problems and challenges. . A project often involves dozens of companies, and the chain is very large, so she believes that now is a good time to do the ecological construction of the Internet of Things. The life cycle of IoT devices will also be extended. Unlike the wearable IoT smart terminals, the modules that enter the meter's water meter and the smart devices that are installed in the car must be used for at least five to ten years. Some devices that are buried with the pipeline. Sensors built with industrial blast furnaces have a life span of fifteen years or more. Shen Lei believes that although the cost of modules or equipment is very low, due to the constant changes in the external environment during long-term use, such as mobile network upgrades, frequency usage redistribution, IoT technology upgrades, etc., will have an impact, so throughout the use It is critical to have very controllable and continuous service to users during the cycle. Especially when IoT equipment is directly related to life and property and quality of life, the equipment can be maintained, safe, and adaptable to the environment. "The one-time sales installation method of IoT chips or modules is completely different from the short-term rapid iteration of mobile phones. In the future Internet of Things and the era of all things, we need to re-adjust the technical direction." Shen Lei said. There are many cloud service providers, many of which need to connect to cloud services, and different vendors have their own requirements for cloud services and client software. How can they seamlessly connect and test with IoT cloud service providers to ensure that they are guaranteed? Devices can seamlessly connect to the cloud for long-term cooperation, which is an ongoing effort by Qualcomm. The starting point for everything is hardware capabilities. Shen Lei said that this capability includes both hardware and software. Massive IoT deployment, from the modem point of view, the initial level of intelligence will not be too high, will focus on the number of development, may invest 1 billion modems at once, but the modems are around the system controller, the system controller is similar to the sensor The server for data input, output, and collection also needs to respond to instructions and interact with the physical world, so Qualcomm has integrated the processor into the main NB-IoT, eMTC modems in the past few years, and made ARM Cortex A7 micro Control the processor and integrate the operating system. In the software part, Qualcomm has done the LTE IoT SDK, including API and software layer, which opens the communication capability, CPU capability and GPS capability through the SDK, making it easy for the device vendors, application developers and cloud service providers who write software around it to access the software. . In addition to the SDK, Qualcomm integrates mainstream IoT cloud service providers, such as Alibaba, WitCloud and other SDK services, into the software, because each cloud service provider's cloud services require client software and its cloud. Services echo each other. Shen Lei said that at the same time, we are further developing other capabilities. One is to upgrade security and trust; the other is to establish remote diagnostics and empowerment capabilities throughout the life of the device to maintain its normal use. For the one-time deployment and long-term use of the Internet of Things, this demand can create new business models. On the eve of this year's World Mobile Congress in Barcelona, ​​Qualcomm launched the Qualcomm Wireless Edge Service, the Qualcomm Wireless Edge Service. Shen Lei said that this new business model reflects the chip capabilities. Every cloud IoT operator has its own device management system. For example, service providers sharing bicycles have already placed 20 million bicycles in various cities in China. Their equipment management system can see the specific location of these bicycles, unlocking or unlocking, paying status and safety of bicycles. Shen Lei said that Qualcomm Infinite Edge Service seamlessly embeds its own equipment management system and data management system into the management system of mainstream cloud service providers. During the entire life cycle of the equipment, remote diagnosis is required without touching the equipment. Remote management. "Qualcomm also has a small cloud that can be considered as an enhancement of the service provider's capabilities. It can see the security situation of our sold, deployed chips, capabilities, new challenges and external environmental changes." Shen Lei said "It can solve the problems of cloud service providers at the same time, so that they can be diagnosed by Qualcomm's capabilities, can master the deployed devices, and then perform verification and device capability adjustment." Speaking of the benefits of this business model, Shen Lei gave an example of a fully intelligent water meter and electricity meter. There are water meters and electricity meters in China's 300-400 million households. If the initial innovation is intelligent, Internet-based access technologies such as NB-IoT and eMTC can be put into operation. When starting operations, only a small amount of data is transmitted. -IoT can be satisfied. If a hacker steals electricity and needs to solve the problem immediately, you can remotely change the working mode to eMTC. You can upgrade the software in a few hours to increase the security. This kind of application scenario that requires remote adjustment can help. Adapt to the uncertainty of the future. After the launch of Qualcomm Wireless Edge Services to the IoT industry chain, several Chinese manufacturers have expressed support, including Alibaba, Baidu, Wisdom Cloud, Japan Shipping, and Mobike. "5G will bring very far-reaching and long-term changes to society and industry, just as important as electricity. And intelligence moves from the cloud to the edge, and even to the sensor, to the physical world, in the process, new business models, The new technology delivery method needs to be invented, and Qualcomm wireless edge service came into being under this new trend." Shen Lei said. However, due to technical and cost reasons, it is not widely used. In recent years, RFID technology has developed by leaps and bounds. With the development of large-scale integrated circuit and network communication technology, RFID technology has entered the commercial application field, and began to develop from the initial low frequency (125kHz) and high frequency (13.56mhz) to uHF (860 ~ 960MHz) and microwave. RFID technology has become one of the most promising information technologies in the new era because of its unique advantages showing great development potential and application space. In both low and high frequency bands, China has independently developed RFID chips in accordance with ISO14443 A, B and ISO15693 standards, which have been successfully applied in major projects such as city bus all-in-one card and second-generation resident ID card. However, in the uHF and microwave field, China started late, technology and products are still relatively short. In this context, this paper studies the design of 915MHz rf card reader. The system can be applied to vehicle monitoring, remote control, telemetry, access control system, identity identification, non-contact radio frequency smart card, wireless 485/232 data communication, safety and fire prevention and other fields. 915MHZ Rubber Antenna,915MHZ Antenna with magnetic base,915MHZ fiberglass antenna Yetnorson Antenna Co., Ltd. , https://www.yetnorson.com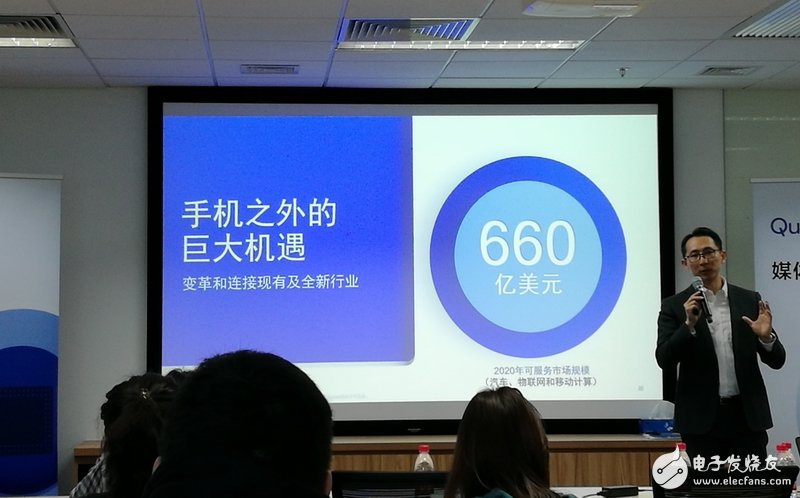
March 12, 2023